Multilayer Laue Lenses (MLLs)
Description and parameters
|
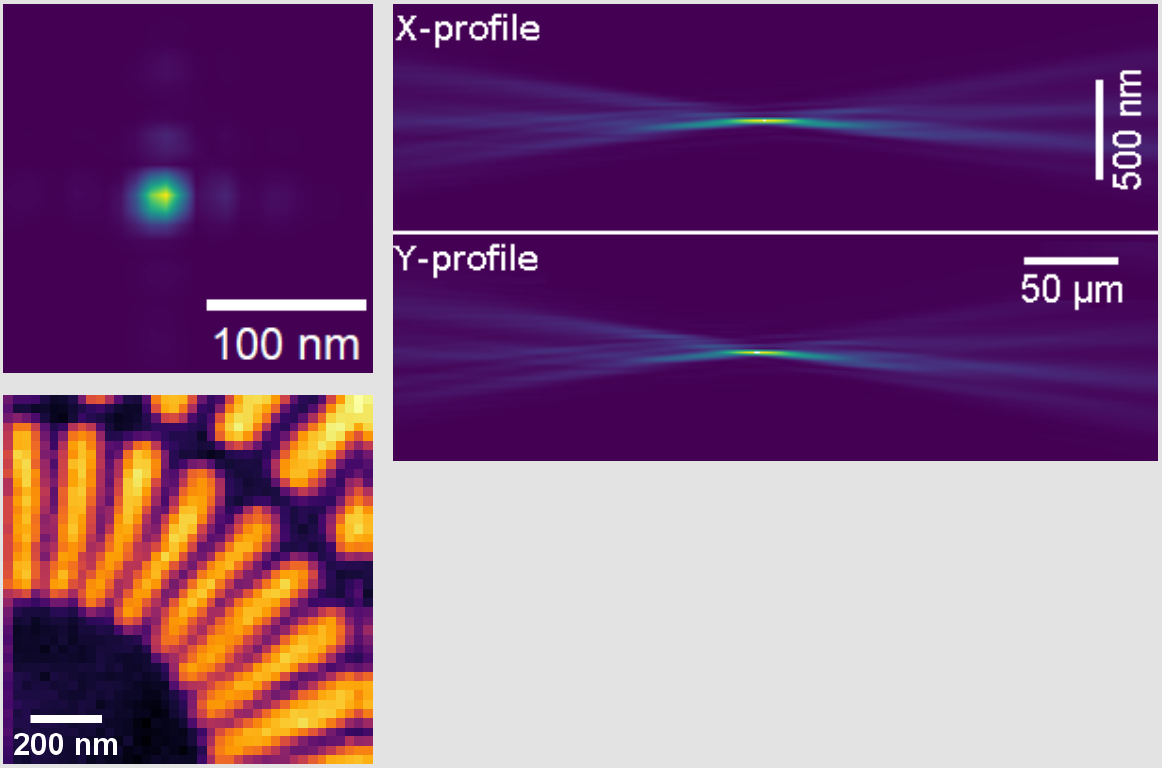
Multilayer Laue Lenses (MLLs) are made from multilayers composed of thousands of individual layers each having a different, very precisely adjusted thickness in the nm-range. When cut into thin slices those MLL work as diffractive optics and can be used as focusing optics similar to Fresnel zone plates. Thus, resolutions of few tens of nanometers and high diffraction efficiencies can be achieved particularly for hard X-rays.
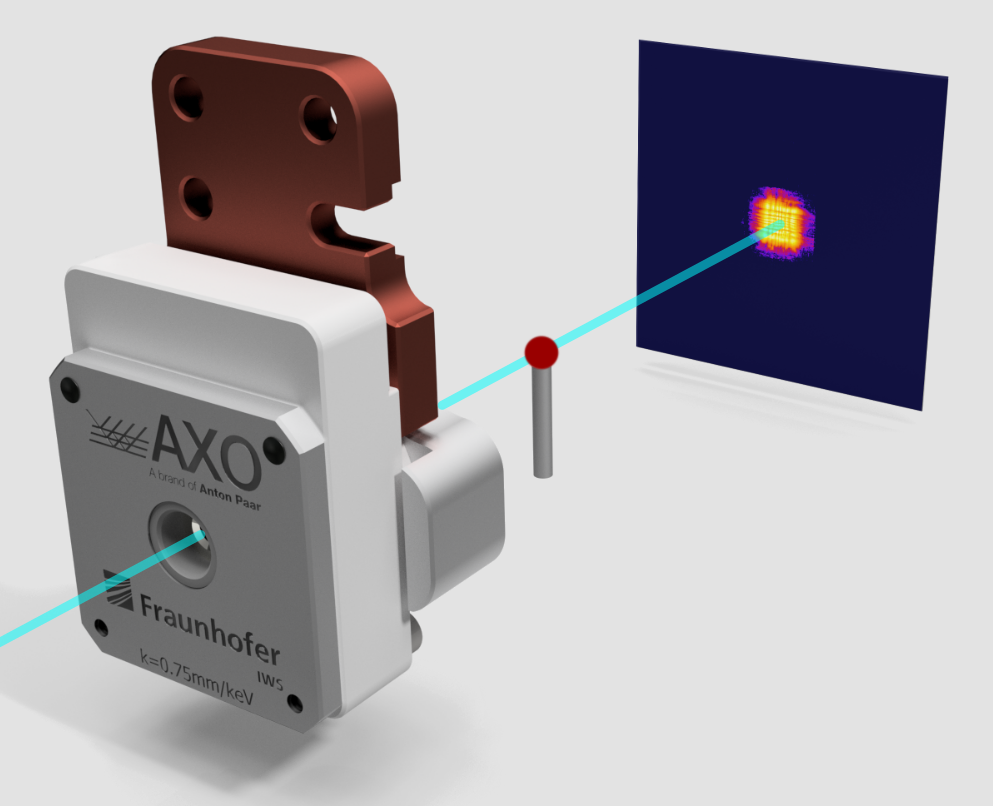
Point focusing can be achieved by combining two MLL slices perpendicularly in a dedicated mount. The resulting lens device is internally aligned to ensure low aberrations. It is as easy to use as a Fresnel zone plate. In order to cope with experimental demands Fraunhofer IWS and AXO DRESDEN have developed MLLs with long working distances. They have been fabricated, tested and used for nano-beam experiments in the framework of long-term proposals at ESRF, Grenoble, and PETRA III, DESY, Hamburg; as well as in other user experiments. Currently, three designs that offer working distances are available. Typical parameters are shown in the table. Although MLLs work over a large photon energy range, each MLL is optimized to a target photon energy in terms of efficiency. Correction phase plates for MLLs to minimize aberrations can be offered together with our partners of XRnanotech (www.xrnanotech.com). Download: MLL prospectus (pdf) |
|